IOT NOTES
Lecture Notes
Today, let’s explore a fascinating analogy between technology waves and a tsunami and what it teaches us about embracing disruptive innovation.
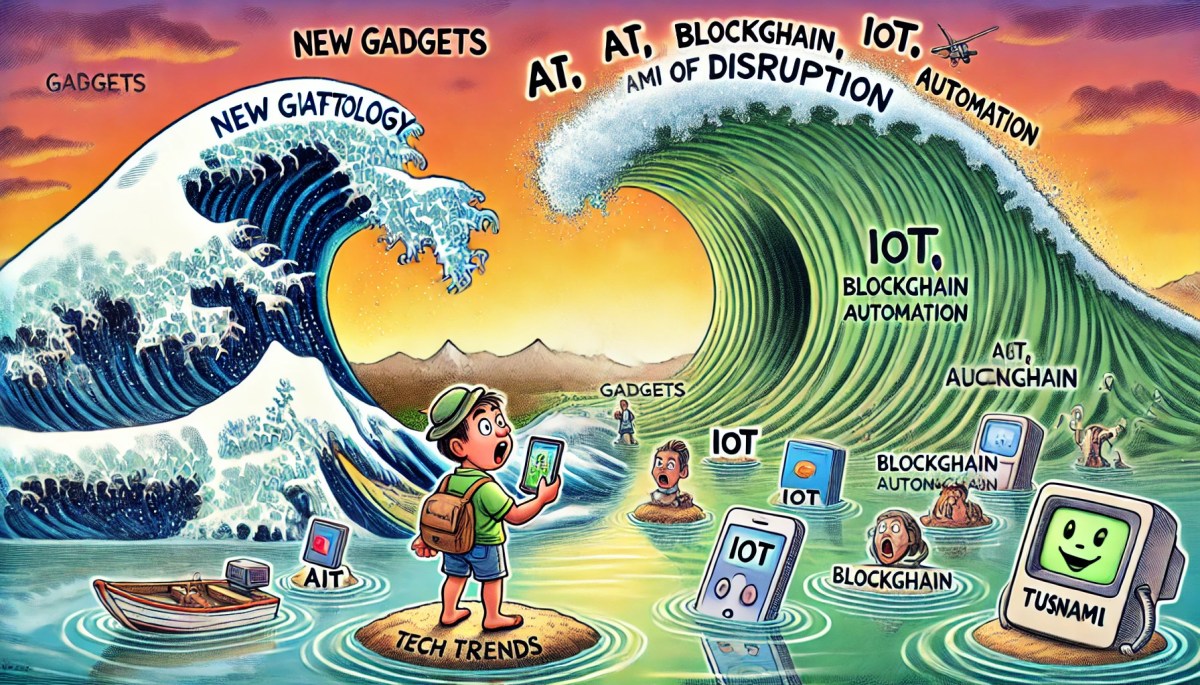
This diagram gives us a vivid understanding of how small technological changes can lead to massive transformations. Let’s break it down step by step.

1. Ripples of Technology
Imagine a drop of water falling into a still pond. That single drop creates ripples that spread outward. Similarly, a single new technology creates small ripples of change. But what happens when multiple waves combine?
- Small Waves: These represent individual technologies making minor changes.
- Combining Waves: When multiple small technologies integrate and interact, they create larger impact waves.
- Tsunami Effect: When these waves grow in size and momentum, they lead to a disruption — a sudden and massive transformation.
Key takeaway: New technologies don’t disrupt on their own; the integration of technologies drives large-scale changes.
2. What Happens Before a Tsunami Hits?
The analogy becomes even more powerful when we think about the moments before a tsunami strikes:
- Sudden Signs: The beach suddenly empties of water, creating a sense of calm before the storm.
- White Waves Appear: The signs of disruption become visible, but people often don’t take them seriously.
- Silence: There’s an eerie pause before the massive wave crashes.
- Unpreparedness: People on the beach are caught off guard and unable to escape.
This is a perfect metaphor for technological revolutions. They often come suddenly, fast, and disastrously for those who are unprepared.
Characteristics of a Revolution:
- Sudden: Changes happen quickly, often without warning.
- Disruptive: Entire industries and systems are transformed.
- Radical Change: Traditional ways of doing things are replaced.
- Complete: The change impacts everyone, leaving no sector untouched.
3. Surfing the IoT Waves
Let’s bring this analogy to life with the Internet of Things (IoT). Imagine you’re a surfer facing the waves of IoT innovation. How do you ride them instead of being overwhelmed?
- Ride the Waves: Stay updated with the latest technological trends. Learn how IoT, AI, and other advancements are shaping industries.
- Be Aware of the Next Wave: Just as a surfer looks for the next big wave, keep an eye on emerging technologies that could disrupt your field.
- Be the Innovator, Not the Laggard: Take action early. Innovate and adapt before the waves of disruption leave you behind.
4. Key Lessons from the Tsunami Analogy
- Disruption is Inevitable: Whether you’re ready or not, technological waves will crash onto the shore of your industry.
- Integration Drives Change: It’s not just one technology but the combination of many that create a tsunami effect.
- Prepare, Don’t React: Those who prepare for change will thrive, while those who wait to react will struggle to keep up.
Final Thoughts
The tsunami analogy reminds us that we can’t stop the waves of technology, but we can learn to ride them. Whether IoT, AI, or another innovation, the key is to stay proactive, informed, and adaptable. Are you ready to surf the waves of change?
Let’s open the floor for questions or reflections on how you can prepare for the next big wave in your industry.
[Download full eBook IoT Notes for free]